CommandService
Overview
The CommandService is a core component of the framework that facilitates the management and synchronization of commands. It primarily provides methods for publishing both full commands and partial commands, allowing for their processing either synchronously or asynchronously, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency and flexibility of command handling within the system.
CommandModule Configuration
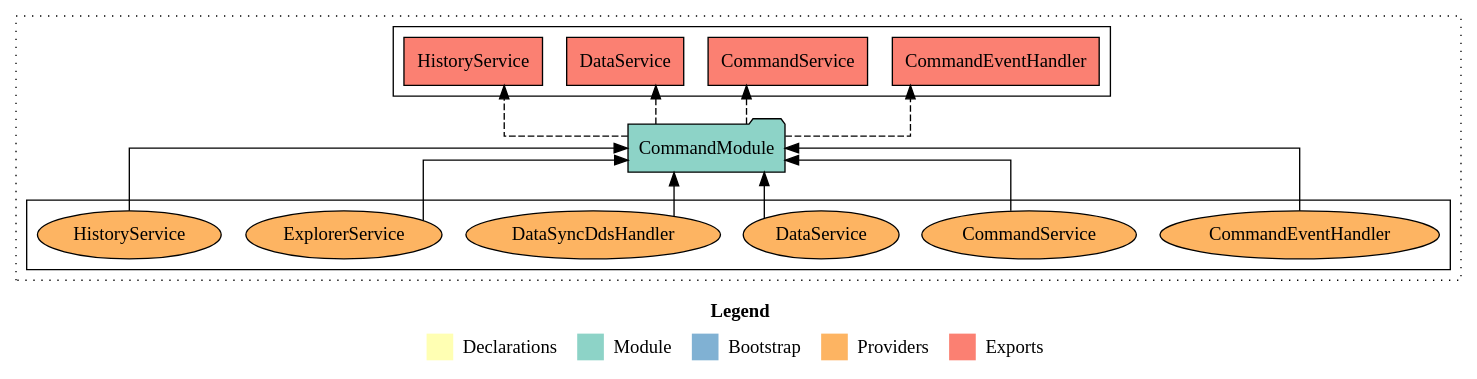
The CommandModule is a dynamic module used to register data sync handlers and provide services associated with a table name. When importing this module, you must provide a specific option for use.
Register Options
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
tableName: string | Provide table name |
skipError?: boolean | Reserved for future use. Not yet implemented. |
dataSyncHandlers?: Type[] | Register data sync handlers |
disableDefaultHandler?: boolean | If set to true, disables the default DynamoDB data sync handler |
Registration Example
import { CommandModule } from '@mbc-cqrs-serverless/core';
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
@Module({
imports: [
CommandModule.register({
tableName: 'cat',
dataSyncHandlers: [CatDataSyncRdsHandler],
}),
],
})
export class CatModule {}
Here, the CommandModule registers with the cat table name and provides the CatDataSyncRdsHandler to the data sync handlers.
Using CommandService
In the example for the method below, assume you import the CommandModule into your module as follows:
import { CommandModule } from "@mbc-cqrs-serverless/core";
import { Module } from "@nestjs/common";
import { CatDataSyncRdsHandler } from "./handler/cat-rds.handler";
import { CatController } from "./cat.controller";
import { CatService } from "./cat.service";
@Module({
imports: [
CommandModule.register({
tableName: "cat",
dataSyncHandlers: [CatDataSyncRdsHandler],
}),
],
controllers: [CatController],
providers: [CatService],
})
export class CatModule {}
Then, the CommandService and DataService will be ready for injection into other services for your use.
For complete CRUD implementation patterns using CommandService, see Service Patterns.
Methods
async publishAsync(input: CommandInputModel, options: ICommandOptions): Promise<CommandModel | null>
Utilize this method to publish a full command, as it will insert the command data into the command table.
The method provides immediate feedback by returning the command data right away, allowing you to proceed without waiting for the command to be processed. Subsequently, the command is handled asynchronously in the background, ensuring that your application remains responsive while the processing occurs.
Return Value: Returns Promise<CommandModel> on success, or Promise<null> when the command is not dirty (no changes detected compared to the existing command).
For example, you can publish a new cat command as bellow:
import {
generateId,
getCommandSource,
VERSION_FIRST,
} from "@mbc-cqrs-serverless/core";
// class CatCommandDto extends CommandDto {}
const catCommand = new CatCommandDto({
pk: catPk,
sk: catSk,
tenantCode,
id: generateId(catPk, catSk),
code,
type: "CAT",
name: attributes.name,
version: VERSION_FIRST,
attributes,
});
const commandSource = getCommandSource(
basename(__dirname),
this.constructor.name,
"createCatCommand"
);
const item = await this.commandService.publishAsync(catCommand, {
source: commandSource,
invokeContext,
});
async publishPartialUpdateAsync( input: CommandPartialInputModel, options: ICommandOptions): Promise<CommandModel>
This method allows you to create new command data based on the previous command with the same pk and sk (primary key) values.
As same as the publishAsync method, the method immediately returns the updated command data without waiting for the command to be processed.
For example, you want to update cat's name:
import { generateId, getCommandSource } from "@mbc-cqrs-serverless/core";
// ...
const catCommand: CommandPartialInputModel = {
pk: catPk,
sk: catSk,
version: storedItem.version,
name: attributes.name,
};
const commandSource = getCommandSource(
basename(__dirname),
this.constructor.name,
"updateCatCommand"
);
const item = await this.commandService.publishPartialUpdateAsync(catCommand, {
source: commandSource,
invokeContext,
});
async publishSync( input: CommandInputModel, options: ICommandOptions): Promise<CommandModel>
This method serves as a synchronous counterpart to the publishAsync method, meaning that it will halt the execution of the code until the command has been fully processed. This ensures that you receive the result of the command before proceeding with any further operations in your code.
For example:
import {
generateId,
getCommandSource,
VERSION_FIRST,
} from "@mbc-cqrs-serverless/core";
// class CatCommandDto extends CommandDto {}
const catCommand = new CatCommandDto({
pk: catPk,
sk: catSk,
tenantCode,
id: generateId(catPk, catSk),
code,
type: "CAT",
name: attributes.name,
version: VERSION_FIRST,
attributes,
});
const commandSource = getCommandSource(
basename(__dirname),
this.constructor.name,
"createCatCommandSync"
);
const item = await this.commandService.publishSync(catCommand, {
source: commandSource,
invokeContext,
});
async publishPartialUpdateSync( input: CommandPartialInputModel, options: ICommandOptions): Promise<CommandModel>
This method is a synchronous version of the publishPartialUpdateAsync method. It will block the execution of the code until the command is processed.
This method requires the version field in the input to match the current version of the existing item. If the item is not found or the version does not match, a BadRequestException is thrown with the message "The input is not a valid, item not found or version not match".
For example, you want to update cat's name:
import { generateId, getCommandSource } from "@mbc-cqrs-serverless/core";
// ...
const catCommand: CommandPartialInputModel = {
pk: catPk,
sk: catSk,
version: storedItem.version,
name: attributes.name,
};
const commandSource = getCommandSource(
basename(__dirname),
this.constructor.name,
"updateCatCommandSync"
);
const item = await this.commandService.publishPartialUpdateSync(catCommand, {
source: commandSource,
invokeContext,
});
async publish(input: CommandInputModel, options: ICommandOptions): Promise<CommandModel | null> deprecated
Deprecated, for removal: This API element is subject to removal in a future version. Use publishAsync method instead.
For example, you can publish a new cat command as bellow:
import {
generateId,
getCommandSource,
VERSION_FIRST,
} from "@mbc-cqrs-serverless/core";
// class CatCommandDto extends CommandDto {}
const catCommand = new CatCommandDto({
pk: catPk,
sk: catSk,
tenantCode,
id: generateId(catPk, catSk),
code,
type: "CAT",
name: attributes.name,
version: VERSION_FIRST,
attributes,
});
const commandSource = getCommandSource(
basename(__dirname),
this.constructor.name,
"createCatCommand"
);
const item = await this.commandService.publish(catCommand, {
source: commandSource,
invokeContext,
});
The method returns the command data.
async publishPartialUpdate( input: CommandPartialInputModel, options: ICommandOptions): Promise<CommandModel | null> deprecated
Deprecated, for removal: This API element is subject to removal in a future version. Use publishPartialUpdateAsync method instead.
This method allows you to create new command data based on the previous command.
For example, you want to update cat's name:
import { generateId, getCommandSource } from "@mbc-cqrs-serverless/core";
// ...
const catCommand: CommandPartialInputModel = {
pk: catPk,
sk: catSk,
version: storedItem.version,
name: attributes.name,
};
const commandSource = getCommandSource(
basename(__dirname),
this.constructor.name,
"updateCatCommand"
);
const item = await this.commandService.publishPartialUpdate(catCommand, {
source: commandSource,
invokeContext,
});
The method returns the updated command data.
async reSyncData(): Promise<void>
If you want to reapply the data sync handler, this method is designed for you to use. You only need to call the function as follows:
await this.commandService.reSyncData();
async getItem(key: DetailKey): Promise<CommandModel>
Retrieves a command item by its primary key. If the sort key does not include a version separator, it automatically calls getLatestItem to get the latest version.
import { DetailKey } from "@mbc-cqrs-serverless/core";
// Get a specific version of a command
const command = await this.commandService.getItem({
pk: "CAT#tenant1",
sk: "CAT#cat001@2", // Includes version number
});
// If no version in sk, automatically gets latest version
const latestCommand = await this.commandService.getItem({
pk: "CAT#tenant1",
sk: "CAT#cat001",
});
async getLatestItem(key: DetailKey): Promise<CommandModel>
Retrieves the latest version of a command item by its primary key. This method uses a lookup algorithm that starts from the data table's version and searches up/down to find the most recent command version.
import { DetailKey } from "@mbc-cqrs-serverless/core";
const latestCommand = await this.commandService.getLatestItem({
pk: "CAT#tenant1",
sk: "CAT#cat001", // Sort key without version
});
if (latestCommand) {
console.log(`Latest version: ${latestCommand.version}`);
}
async getNextCommand(currentKey: DetailKey): Promise<CommandModel>
Retrieves the next version of a command based on the current command's key. This is useful for processing command chains or implementing retry logic.
import { DetailKey } from "@mbc-cqrs-serverless/core";
const currentKey: DetailKey = {
pk: "CAT#tenant1",
sk: "CAT#cat001@2",
};
const nextCommand = await this.commandService.getNextCommand(currentKey);
// Returns command with sk: "CAT#cat001@3" if exists
async updateStatus(key: DetailKey, status: string, notifyId?: string): Promise<void>
Updates the status of a command and sends an SNS notification. This is commonly used to update task or process statuses and notify subscribers of the change.
import { DetailKey } from "@mbc-cqrs-serverless/core";
const key: DetailKey = {
pk: "CAT#tenant1",
sk: "CAT#cat001@1",
};
// Update status and send SNS notification
await this.commandService.updateStatus(key, "COMPLETED");
// With custom notification ID
await this.commandService.updateStatus(key, "FAILED", "custom-notify-id");
The SNS notification payload includes:
action:"command-status"pk,sk: The command keytable: The command table nameid: Notification ID (custom or auto-generated)tenantCode: Extracted from pkcontent: Object containingstatusandsource
async duplicate(key: DetailKey, options: ICommandOptions): Promise<CommandModel>
Creates a duplicate of an existing command with an incremented version number. The duplicated command will have source set to "duplicated" and updated metadata (timestamp, user, IP).
import { DetailKey, getCommandSource } from "@mbc-cqrs-serverless/core";
import { basename } from "path";
const key: DetailKey = {
pk: "CAT#tenant1",
sk: "CAT#cat001@1",
};
const commandSource = getCommandSource(
basename(__dirname),
this.constructor.name,
"duplicateCatCommand"
);
const duplicatedCommand = await this.commandService.duplicate(key, {
source: commandSource,
invokeContext,
});
// The duplicated command has:
// - version incremented by 1
// - source set to "duplicated"
// - updated timestamps and user info
async updateTaskToken(key: DetailKey, token: string): Promise<CommandModel>
Stores an AWS Step Functions task token on a command item. This is used when integrating with Step Functions to enable callback patterns.
import { DetailKey } from "@mbc-cqrs-serverless/core";
const key: DetailKey = {
pk: "CAT#tenant1",
sk: "CAT#cat001@1",
};
// Store the Step Functions task token
await this.commandService.updateTaskToken(key, event.taskToken);
// Later, use the token to send task success/failure
// via SendTaskSuccessCommand or SendTaskFailureCommand
async updateTtl(key: DetailKey): Promise<any | null>
Updates the TTL (Time To Live) of the previous version of a command. This is typically used internally to manage command history retention. Returns null if the version is too low or the previous command doesn't exist.
import { DetailKey } from "@mbc-cqrs-serverless/core";
const key: DetailKey = {
pk: "CAT#tenant1",
sk: "CAT#cat001@3", // Version 3
};
// Updates TTL of version 2 (previous version)
const result = await this.commandService.updateTtl(key);
This method is primarily used internally by the framework for command history management. Direct usage is rarely needed in application code.
dataSyncHandlers (getter): IDataSyncHandler[]
Returns the array of registered data sync handlers for this CommandService instance. This is useful when you need to inspect or iterate over the handlers programmatically.
// Get all registered data sync handlers
const handlers = this.commandService.dataSyncHandlers;
handlers.forEach((handler) => {
console.log(`Handler: ${handler.constructor.name}, Type: ${handler.type}`);
});
getDataSyncHandler(name: string): IDataSyncHandler | undefined
Retrieves a specific data sync handler by its class name. Returns undefined if no handler with the specified name is found.
// Get a specific handler by name
const rdsHandler = this.commandService.getDataSyncHandler('CatDataSyncRdsHandler');
if (rdsHandler) {
// Use the handler directly
await rdsHandler.up(commandModel);
}
isNotCommandDirty(item: CommandModel, input: CommandInputModel): boolean
Compares an existing command item with a new input to determine if there are any actual changes. Returns true if the command is NOT dirty (no changes), returns false if there ARE changes.
This method is used internally by publish methods to skip unnecessary writes when no changes are detected. You can also use it directly to check if an update would result in any changes before calling publish.
// Check if an update would result in changes
const existingCommand = await this.commandService.getItem({ pk, sk });
if (existingCommand && this.commandService.isNotCommandDirty(existingCommand, newInput)) {
// No changes detected, skip the update
console.log('Command has no changes, skipping update');
return existingCommand;
}
// Proceed with the update
const result = await this.commandService.publishAsync(newInput, options);
tableName (getter/setter): string
Gets or sets the DynamoDB table name for this CommandService instance. The table name is configured when registering the CommandModule, but can be changed at runtime if needed.
// Get the current table name
const currentTable = this.commandService.tableName;
console.log(`Operating on table: ${currentTable}`);
// Set a different table name
this.commandService.tableName = 'another-table';
Changing the table name at runtime is an advanced use case. In most applications, you should configure the table name through CommandModule.register() and not change it afterwards.