Glossary
This glossary provides definitions for key terms and concepts used throughout the MBC CQRS Serverless framework documentation.
Design Patterns
CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation)
The command query responsibility segregation (CQRS) pattern separates the data mutation, or the command part of a system, from the query part. You can use the CQRS pattern to separate updates and queries if they have different requirements for throughput, latency, or consistency. The CQRS pattern splits the application into two parts—the command side and the query side. The command side handles create, update, and delete requests. The query side runs the query part by using the read replicas.
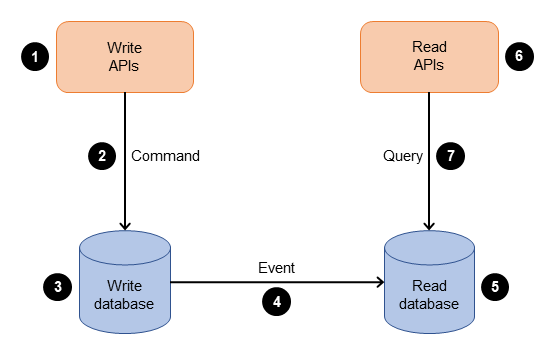
See: CQRS pattern
Event Sourcing
The event sourcing pattern is typically used with the CQRS pattern to decouple read from write workloads, and optimize for performance, scalability, and security. Data is stored as a series of events, instead of direct updates to data stores. Microservices replay events from an event store to compute the appropriate state of their own data stores. The pattern provides visibility for the current state of the application and additional context for how the application arrived at that state. The event sourcing pattern works effectively with the CQRS pattern because data can be reproduced for a specific event, even if the command and query data stores have different schemas.
Optimistic Locking
A concurrency control mechanism that allows multiple transactions to proceed without locking resources. Before committing, the system checks if another transaction has modified the data. In MBC CQRS Serverless, this is implemented using version numbers - each update must include the current version, and the update fails if the version doesn't match.
Domain-Driven Design (DDD)
A software design approach that focuses on modeling software based on the business domain. Key concepts include entities, value objects, aggregates, and bounded contexts. MBC CQRS Serverless uses DDD principles to structure modules and entities.
Aggregate
A cluster of domain objects that can be treated as a single unit. An aggregate has a root entity (the aggregate root) and boundary that defines what's inside the aggregate. In MBC CQRS Serverless, each command table typically represents an aggregate.
Framework Concepts
Command
A request to change the state of the system. Commands are processed by the command side of the CQRS pattern. In MBC CQRS Serverless, commands are published using CommandService and stored in DynamoDB command tables.
Command Table
A DynamoDB table that stores the command (write) model. Contains the full history of changes with version tracking. Data flows from command tables to data tables via DynamoDB Streams.
Data Table
A DynamoDB table that stores the data (read) model. Contains the current state of entities, optimized for queries. Updated automatically when commands are processed.
Data Sync Handler
A handler that processes DynamoDB Stream events to synchronize data between tables or to external systems like RDS. Implements the IDataSyncHandler interface.
Invoke Context
The context object passed to service methods containing user information, tenant context, and request metadata. Created from the Lambda event and used for authorization and auditing.
Partition Key (PK)
The primary key component in DynamoDB that determines data distribution across partitions. In MBC CQRS Serverless, typically formatted as TYPE#tenantCode (e.g., ORDER#tenant001).
Sort Key (SK)
The secondary key component in DynamoDB that enables range queries within a partition. In MBC CQRS Serverless, typically formatted as TYPE#code for data tables or TYPE#code#vN for command tables.
Tenant
An isolated organizational unit in a multi-tenant application. Each tenant has its own data partition identified by a tenant code. Tenants share the application infrastructure but have completely isolated data.
Version
A number that tracks the revision history of an entity. Incremented on each update. Used for optimistic locking to prevent concurrent update conflicts.
AWS Services
Amazon DynamoDB
A fully managed NoSQL database service that provides fast and predictable performance with seamless scalability. MBC CQRS Serverless uses DynamoDB as the primary data store for both command and data tables.
DynamoDB Streams
A feature that captures data modification events in DynamoDB tables. Used by MBC CQRS Serverless to trigger data synchronization between command and data tables, and to external systems.
AWS Lambda
A serverless compute service that runs code in response to events. MBC CQRS Serverless uses Lambda functions for API handlers, event processors, and background tasks.
Amazon Cognito
A service that provides user authentication, authorization, and user management. MBC CQRS Serverless uses Cognito for user authentication and JWT token validation.
AWS Step Functions
A serverless orchestration service that lets you combine Lambda functions and other AWS services. Used in MBC CQRS Serverless for long-running workflows like data imports and batch processing.
Amazon SES (Simple Email Service)
An email platform that provides an easy, cost-effective way to send and receive email. Used by MBC CQRS Serverless for notification emails.
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service)
Object storage service for storing and retrieving any amount of data. Used for file uploads, exports, and static asset storage.
Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service)
A fully managed message queuing service. Used for asynchronous processing and decoupling components.
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service)
A managed relational database service. Used in MBC CQRS Serverless for complex queries that require SQL joins and aggregations.
AWS CDK (Cloud Development Kit)
An open-source software development framework to define cloud infrastructure in code. MBC CQRS Serverless uses CDK for infrastructure provisioning.
API Gateway
A fully managed service for creating, publishing, and managing APIs. Provides the HTTP endpoints for MBC CQRS Serverless applications.
CloudWatch
A monitoring and observability service. Used for logging, metrics, and alarms in MBC CQRS Serverless applications.
Tooling & Libraries
NestJS
Nest (NestJS) is a framework for building efficient, scalable Node.js server-side applications. It uses progressive JavaScript, is built with and fully supports TypeScript (yet still enables developers to code in pure JavaScript) and combines elements of OOP (Object Oriented Programming), FP (Functional Programming), and FRP (Functional Reactive Programming).
See: NestJS Documentation
Serverless Framework
The Serverless Framework consists of a Command Line Interface and an optional Dashboard, and helps you deploy code and infrastructure together on Amazon Web Services, while increasingly supporting other cloud providers. The Framework is a YAML-based experience that uses simplified syntax to help you deploy complex infrastructure patterns easily, without needing to be a cloud expert.
Prisma
Prisma is an ORM for Node.js and TypeScript that serves as an alternative to writing plain SQL or using other database access tools, such as Knex or Sequelize. It simplifies database access and management by providing developers with a type-safe query builder and auto-generator.
See: Prisma Documentation
class-validator
A validation library that uses decorators for defining validation rules on class properties. Used in MBC CQRS Serverless for request DTO validation.
class-transformer
A library for transforming plain objects into class instances and vice versa. Works with class-validator for type-safe request handling.
API Concepts
DTO (Data Transfer Object)
An object that carries data between processes. In MBC CQRS Serverless, DTOs define the structure of API request and response bodies, typically with validation decorators.
Entity
A domain object with a distinct identity that persists over time. In MBC CQRS Serverless, entities are TypeScript classes that define the structure of data stored in DynamoDB.
Controller
A class that handles incoming HTTP requests. In NestJS/MBC CQRS Serverless, controllers define API routes and delegate business logic to services.
Service
A class that contains business logic. In MBC CQRS Serverless, services orchestrate data operations using CommandService and DataService.
Module
A class annotated with @Module() decorator that organizes the application structure. Each feature area has its own module containing controllers, services, and providers.
Guard
A class that determines whether a request should be handled by the route handler. Used for authentication and authorization.
Pipe
A class that transforms or validates input data before it reaches the route handler. Used for validation and data transformation.
Middleware
A function called before the route handler. Can perform operations like logging, authentication, and request modification.
Data Operations
Publish (publishAsync/publishSync)
Create a new entity. publishAsync processes asynchronously via DynamoDB Streams, while publishSync processes synchronously.
Partial Update (publishPartialUpdateAsync/publishPartialUpdateSync)
Update specific fields of an existing entity without providing all fields. Requires version for optimistic locking.
Soft Delete
Mark an entity as deleted (isDeleted: true) without physically removing it from the database. Allows for data recovery and audit trails.
Hard Delete
Physically remove an entity from the database. Typically done with TTL (Time-to-Live) or explicit delete operations.
Sequence
An auto-incrementing number generator. Used to generate unique codes like order numbers. Can be rotated by day, month, or year.
Architecture Terms
Cold Start
The initial startup time of a Lambda function when it's invoked after being idle. Can affect latency for the first request.
Warm Start
Subsequent invocations of a Lambda function that reuse an existing execution environment. Faster than cold starts.
Idempotency
The property where an operation produces the same result regardless of how many times it's executed. Critical for retry logic and event handling.
Eventually Consistent
A consistency model where reads may not immediately reflect the latest write, but will eventually become consistent. Default for DynamoDB reads.
Strongly Consistent
A consistency model where reads always return the most recent write. Available for DynamoDB reads with higher latency.
TTL (Time-to-Live)
A DynamoDB feature that automatically deletes items after a specified timestamp. Used for temporary data and automatic cleanup.
GSI (Global Secondary Index)
An index with a partition key and optional sort key different from the table's primary key. Enables efficient queries on alternative access patterns.
LSI (Local Secondary Index)
An index with the same partition key as the table but a different sort key. Must be created at table creation time.
Security Terms
JWT (JSON Web Token)
A compact, URL-safe token format for securely transmitting claims. Used by Cognito for authentication tokens.
IAM (Identity and Access Management)
AWS service for managing access to AWS resources. Defines permissions for Lambda functions and other services.
RBAC (Role-Based Access Control)
An access control method where permissions are assigned to roles, and users are assigned to roles. Implemented via Cognito groups.
See Also
- Architecture Overview - System architecture explanation
- CQRS Flow - Detailed CQRS implementation
- Key Patterns - PK/SK design patterns